用RNN来预测学习sinx曲线
1 | #author:victor |
运行效果
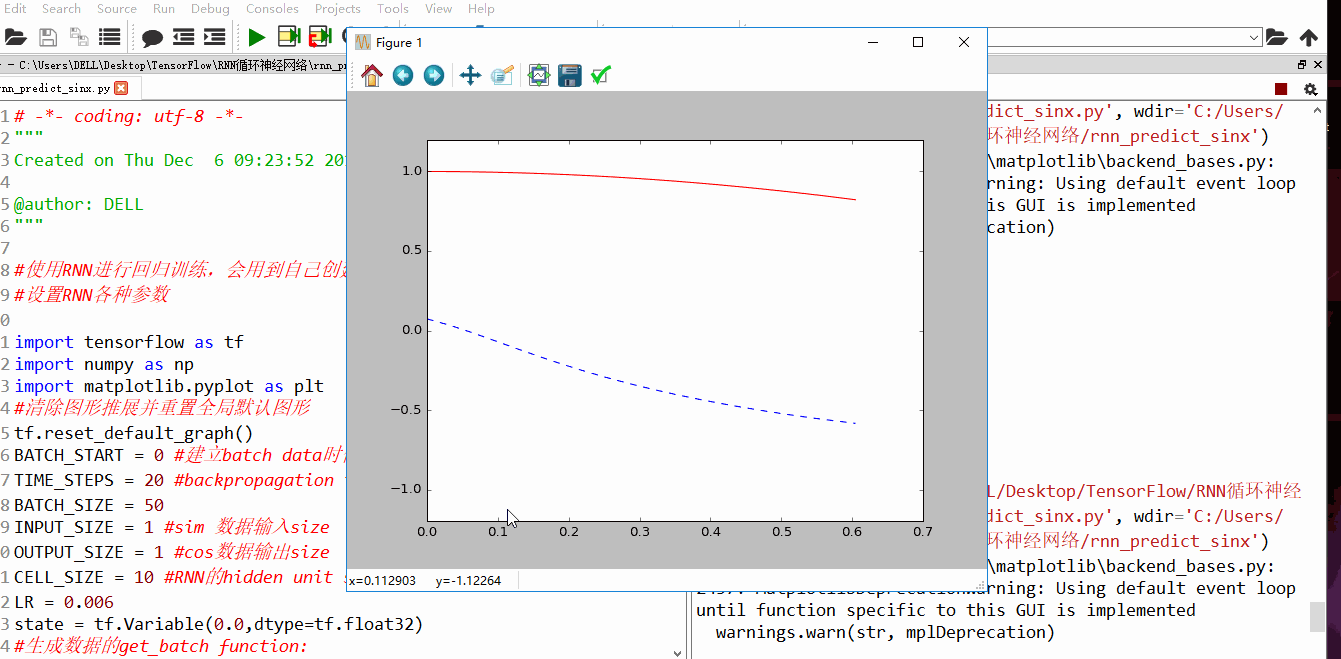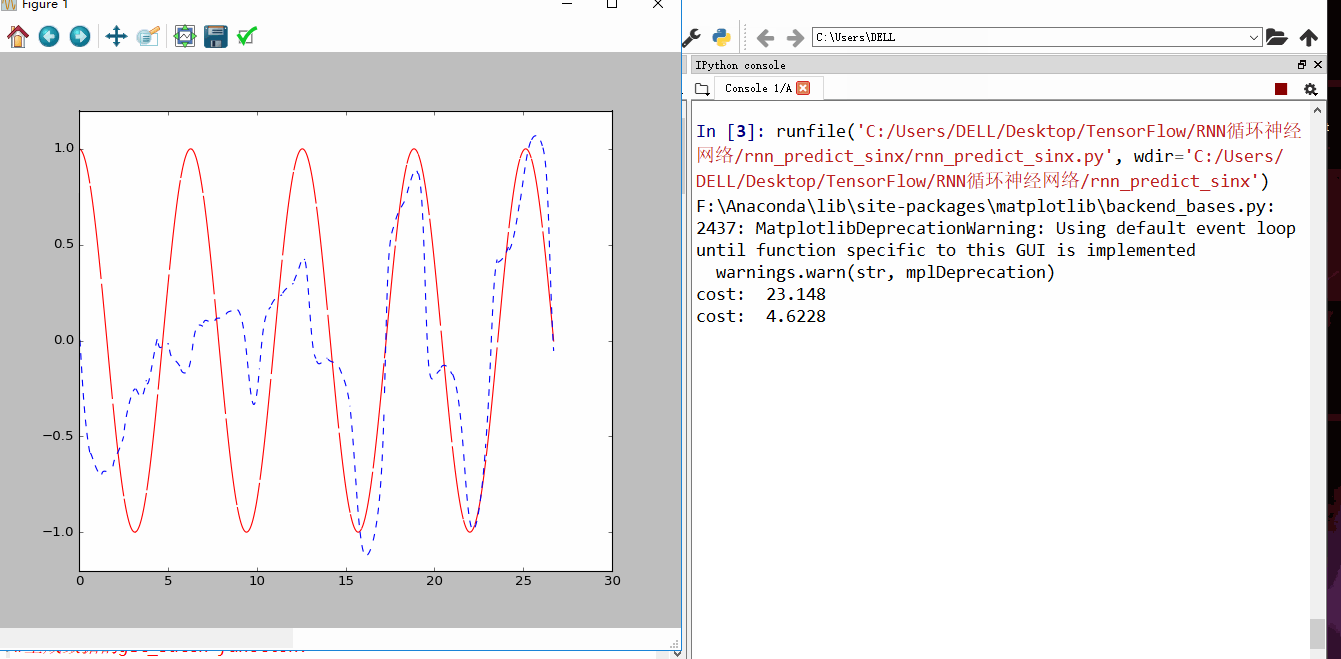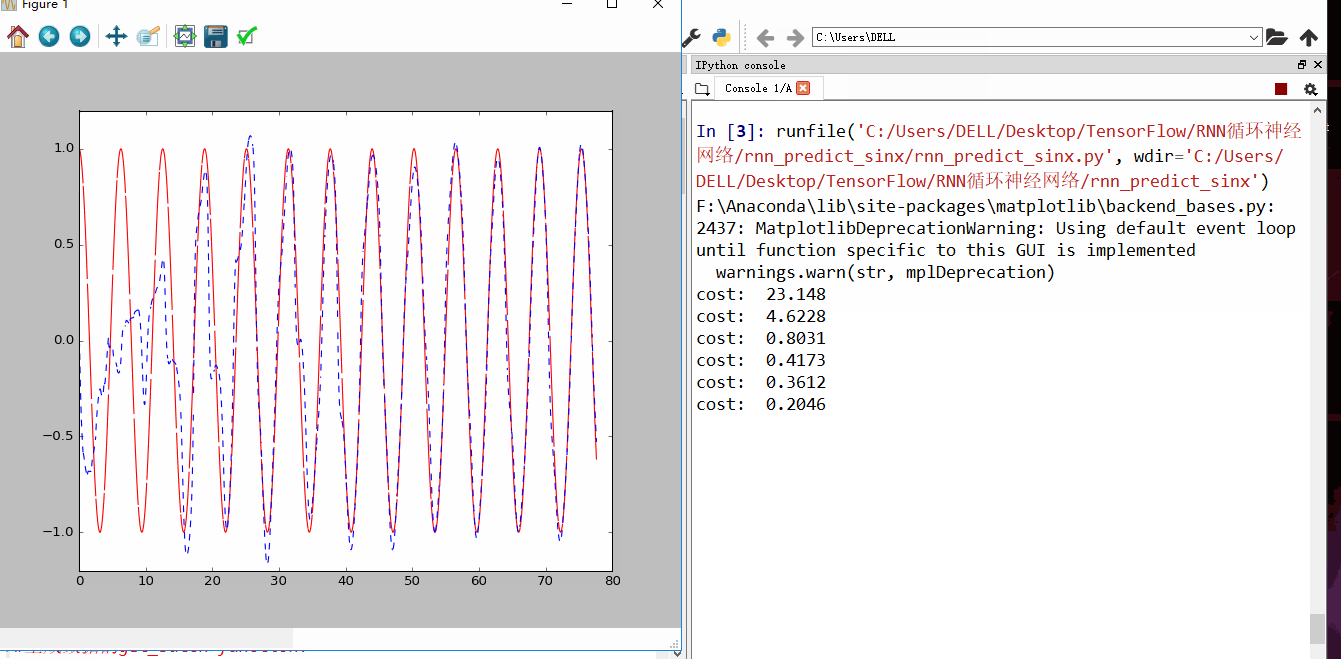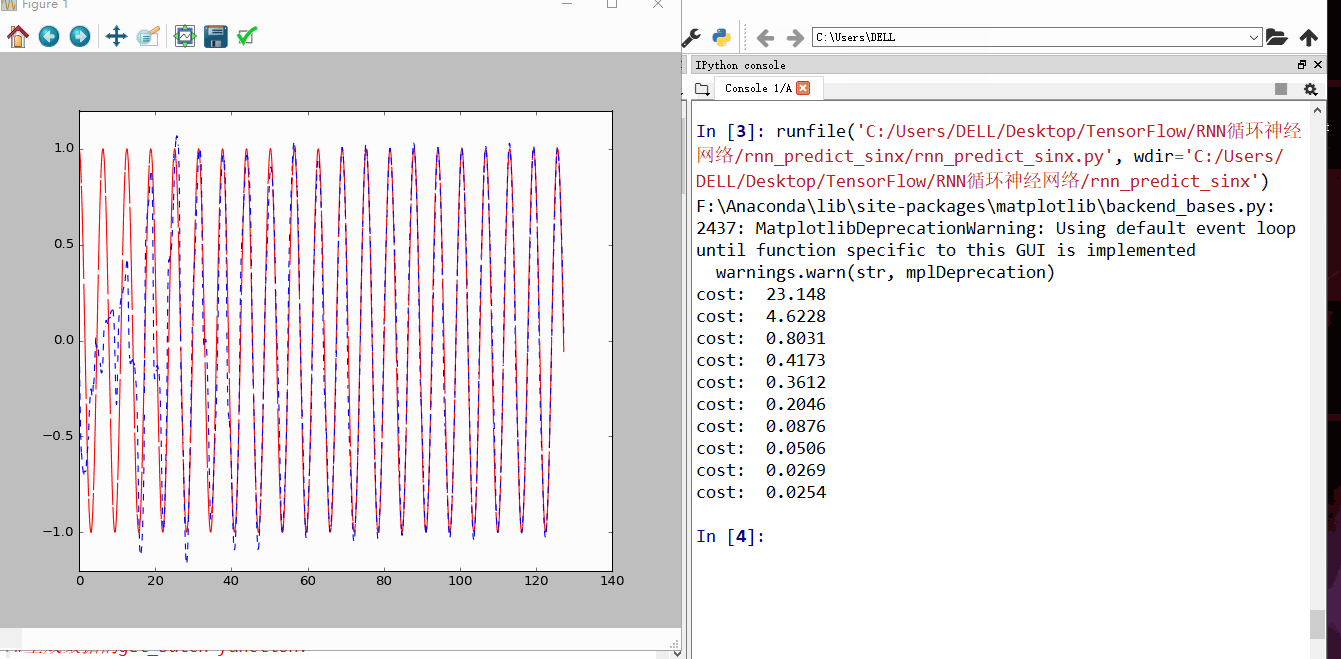
发现刚开始RNN蓝色曲线为预测去年,并不是很重合,随着慢慢的RNN训练,到60以后,预测曲线和实际曲线基本吻合。
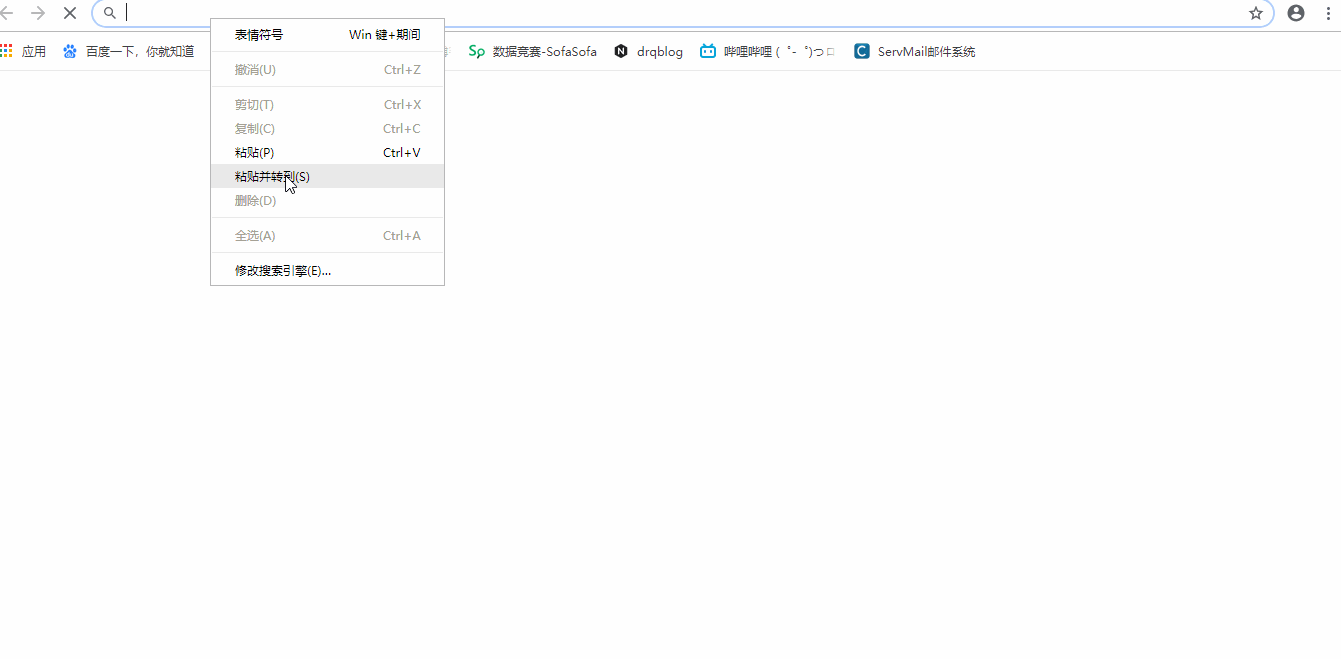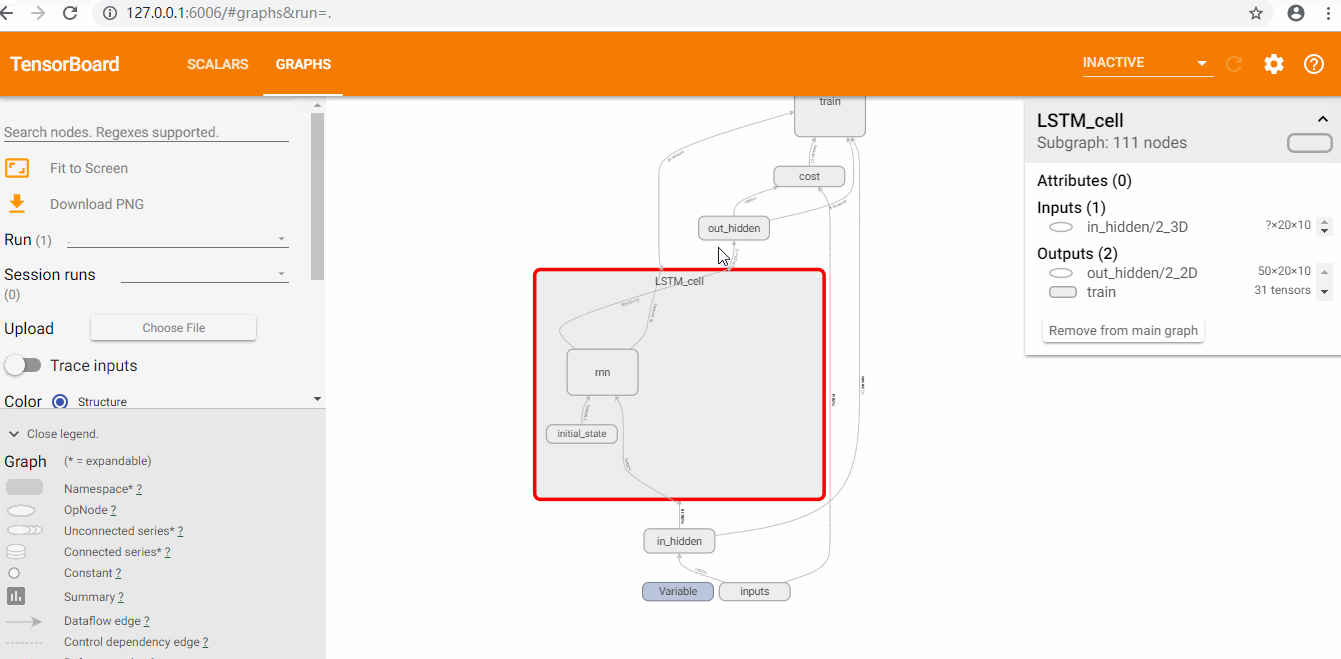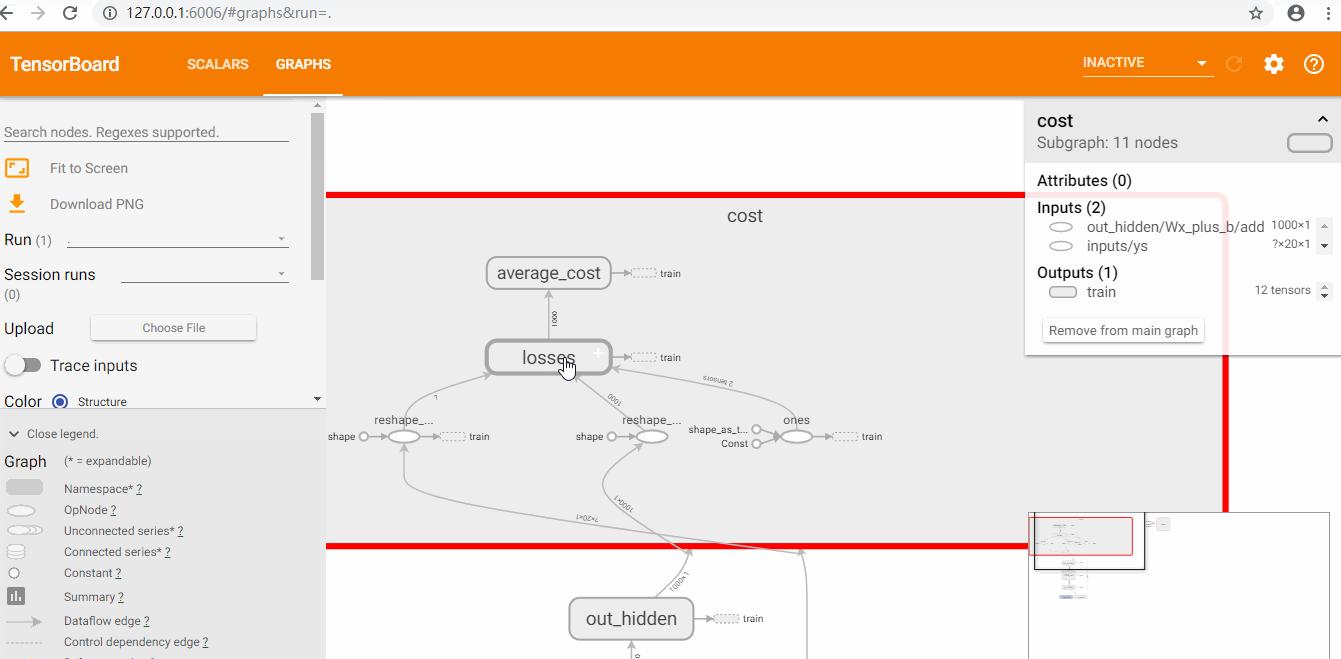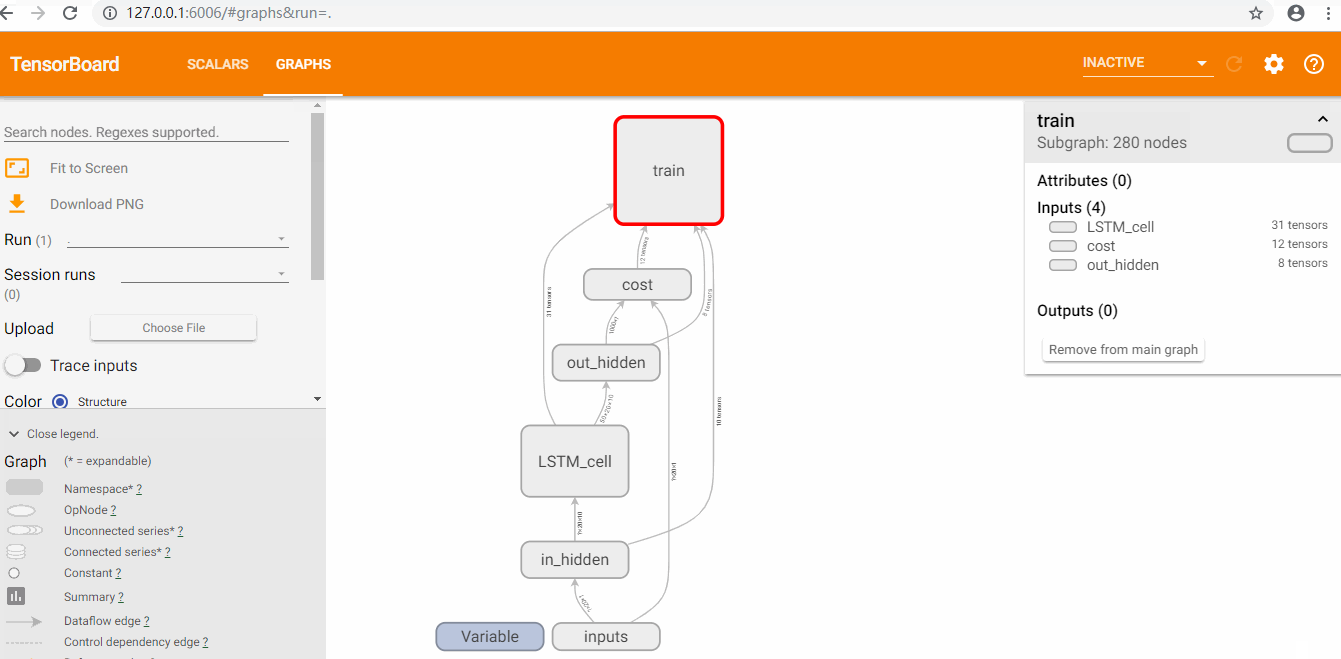
用Tensorboard查看loss和graph
使用tensorboard

查看loss和graph

1 | #author:victor |

发现刚开始RNN蓝色曲线为预测去年,并不是很重合,随着慢慢的RNN训练,到60以后,预测曲线和实际曲线基本吻合。
使用tensorboard

查看loss和graph
